Mark-10 IMF002 Materials Testing Calculations Module for F series test stand.
Characterize and analyze the behavior of materials, components, and assemblies with a suite of materials testing calculations, including:
- Stress and strain
- Tensile strength
- Shear strength
- Young’s modulus (auto-calculate or manually draw)
- Yield point
- Offset yield (user-specified percentage)
- Rupture
- Percent elongation
- Flexural modulus
- Force per unit width
- Wide variety of results based on the above calculations, such as stress at maximum strain, strain at rupture, etc.
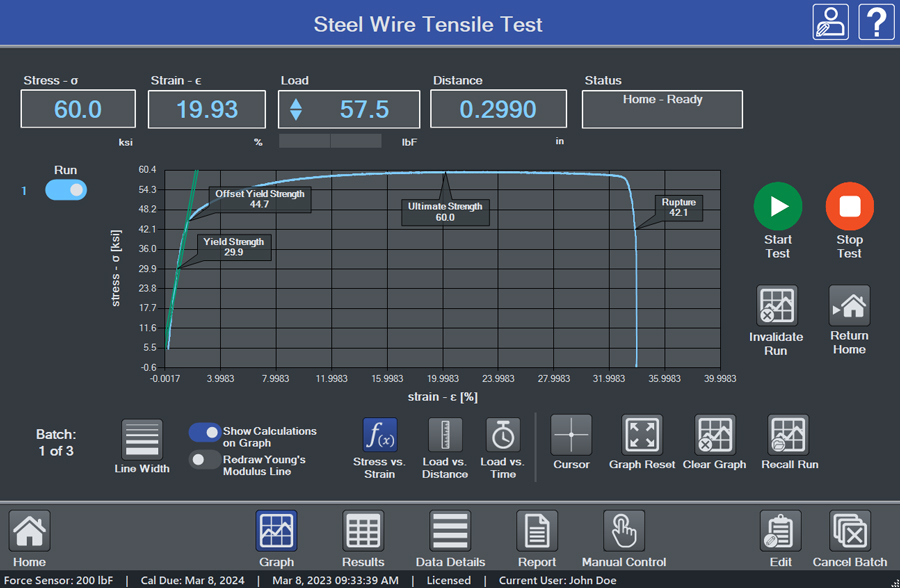
IntelliMESUR® formats calculations into a Results table, with corresponding statistics for multiple runs. View a stress-strain curve with annotated calculations. Display up to 10 runs simultaneously for visual comparison.
Common materials testing calculations include:
Stress
Stress equals force divided by the cross-sectional area of the sample, commonly measured in psi or MPa.
Strain
Strain is the percentage deformation of a sample while under load, measured from its original length between the grips.
Young’s Modulus
Young’s modulus, otherwise known as modulus of elasticity, is the slope of the elastic portion of a stress-strain curve.
Yield Strength
Yield strength is the amount of stress that can be developed in a material without causing plastic deformation; in other words, the transition point from elastic to plastic behavior.
Offset Yield Strength
Offset yield strength approximates a stress just beyond the elastic limit. Draw a parallel line to the Young’s Modulus, offset by a specified amount, commonly 0.2%, and identify the intersection point along the stress-strain curve.
Ultimate Strength
Ultimate strength refers to the maximum observed stress during the test.
Rupture
Rupture is the amount of stress at which the sample breaks. A break can be defined as a specified percentage of drop from the ultimate strength.
Note: Calculations are not available for multi-step tests.